What Is The Perfect Answer To Inferior Calcaneal Spur
Overview
A heel spur is an overgrowth of bone that resembles a hook on the bottom of the foot. It is a reaction to stress placed on the thick connective tissue on the bottom of the foot (plantar fascia) that helps maintain the arches of the foot. Over-stress can stem from improper support of the feet. A heel spur is often accompanied by a bursitis that is a major contributor to pain.
Causes
When a bone is subjected to pressure, rubbing, or other stress over long periods, it tries to repair itself by building extra bone. This extra bone is what is referred to as a ?spur?. Many form as part of the aging process when cartilage breaks down in the joints.

Symptoms
Major symptoms consist of pain in the region surrounding the spur, which typically increases in intensity after prolonged periods of rest. Patients may report heel pain to be more severe when waking up in the morning. Patients may not be able to bear weight on the afflicted heel comfortably. Running, walking, or lifting heavy weight may exacerbate the issue.
Diagnosis
The proper diagnosis of a heel spur often requires an X-ray. To make this process as convenient for his patients as possible, most clinics have an on-site digital X-ray and diagnostic ultrasound machines. This can make it unnecessary for patients to visit diagnostic imaging centers, allowing patients to receive more expedient treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are both conservative and surgical heel spur treatment options. Because the heel pain caused by heel spurs is symptomatic of inflammation, the first step is to ice the area in hopes to reduce the inflammation. The next step is to see our orthopedic specialist to prescribe an appropriate treatment plan. Some conservative treatment options might include Anti-inflammatory medications. Shoe orthotics. Shoe inserts. If conservative treatments are not working, surgery may be required to remove the heel spur. As in all cases of heel pain, it is important to see an orthopedic doctor who specializes in foot and ankle pain.
Surgical Treatment
Usually, heel spurs are curable with conservative treatment. If not, heel spurs are curable with surgery, although there is the possibility of them growing back. About 10% of those who continue to see a physician for plantar fascitis have it for more than a year. If there is limited success after approximately one year of conservative treatment, patients are often advised to have surgery.
Prevention
A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight.
What May Cause Calcaneal Spur

Overview
The term heel spur generally refers more specifically to a heel spur, also known as a calcaneal spur. These calcium growths form around the tendons and ligaments of the foot and eventually become attached to the heel bone. The spurs then continue to grow, piercing the skin of the foot and causing pain and discomfort. When left untreated the spur can continue to grow causing agonizing pain and even immobilizing the patient.
Causes
Faulty foot structures such as abnormal growths, different leg lengths, and unhealed injuries and haveinf flat feet or high arches. Muscle imbalances tight, weak or shortened muscles in your foot, plantar fascia, ankle, calf and hamstring. Over pronation can cause imbalance in foot mechanics which puts excess pressure on the plantar fascia. Poor biomechanics affect the way your foot hits the ground. If you overpronate (feet roll inward) you tend to have flat feet (pes planus), which increases stress on the heel bone. Regular shoes or high heels that are too tight or don't support your heel or arch affect the distribution of your body weight on your foot. Health conditions such as obesity, inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis), bursitis, neuroma (nerve growths), gout, diabetes, Haglund's deformity, and Achilles tendinitis can also instigate the problem. Running or jogging on hard surfaces, repetative striking of the heel bone.

Symptoms
The spur itself is not painful, however, if it is sharp and pointed it can poke into soft tissue surrounding the spur itself. As the bone spur irritates the tissue, inflammation and bruising can occur leading to heel pain. Heel spurs can affect your ability to do your usual work and/or activities, and can also trap and irritate the nerves in your heel area. They can change the way you walk, and can lead to knee, hip and low back injuries. If severe, they may require medical intervention.
Diagnosis
Sharp pain localized to the heel may be all a doctor needs to understand in order to diagnose the presence of heel spurs. However, you may also be sent to a radiologist for X-rays to confirm the presence of heel spurs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Since heel spurs are not an indication of pain themselves unless fractured, treatment is usually aimed at the cause of the pain which in many cases is plantar fasciosis. Treatment of plantar fasciiosis includes; rest until the pain subsides, special stretching exercises and if required orthotics may be prescribed.
Surgical Treatment
In some cases, heel spurs are removed by surgery after an X-ray. While the surgery is typically effective, it?s a timely and expensive procedure. Even after surgery, heel spurs can re-form if the patient continues the lifestyle that led to the problem. These reasons are why most people who develop painful heel spurs begin looking for natural remedies for joint and bone pain. Surgery isn?t required to cure a heel spur. In fact, more than 90 percent of people get better with nonsurgical treatments. If nonsurgical methods fail to treat symptoms of heel spurs after 12 months, surgery may be necessary to alleviate pain and restore mobility.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bursitis Of The Foot
Overview
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis. This bursa is located at the back of the heel. Bursitis in this area is often associated with conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritis. It can occur in healthy individuals who wear improperly fitted shoes. Symptoms include painful swelling that develops at the back of the heel. Calcaneal Bursitis. This bursa is located at the sole or bottom of the heel. Inflammation usually produces pain in the heel when standing. Causes include heel spurs, excess weight, injury, and wearing improperly fitted shoes.
Causes
Although rare, bursitis also may be caused by an infection, known as septic bursitis. This is a serious medical condition that requires antibiotics to treat the infection and prevent its spread to other points in the body or the bloodstream. Septic bursitis may cause the back of the ankle to become red or hot. The person may also get the chills or fever and may feel sick and tired. Typically this type of bursitis would be suspected if there has been any history of an open wound in the area, such as a blister.
Symptoms
Pain at the back of the heel, especially with jumping, hopping, tip-toeing, walking or running uphill or on soft surfaces. If tendonitis is also present, the pain can radiate away from the bursa. Direct pressure on the bursa will exacerbate the pain and should be avoided if possible. Tenderness and swelling which might make it difficult to wear certain shoes on the feet. As the bursa becomes more inflamed you will experience swelling and warmth. In severe cases, the bursa will appear as a bump, called a "pump bump", and is usually red, and extremely tender. Swelling can cause difficulties moving as the range of motion in the ankle can be affected. Limping due to the pain may occur. If you press on both sides of the inflamed heel, there may be a firm spongy feeling. Weakness in the tendons and muscles surrounding the bursa can develop as the pain worsens and the inflammation in the area spreads. Possibly a fever if you are suffering from septic bursitis (You will need to see a doctor for medication to get rid of the infection). Pain at the back of the heel makes it difficult to continue wearing shoes, especially high heels with straps or shoes that don't fit properly.
Diagnosis
When a patient has pain in a joint, a careful physical examination is needed to determine what type of movement is affected and if there is any swelling present. Bursitis will not show up on x-rays, although sometimes there are also calcium deposits in the joint that can be seen. Inserting a thin needle into the affected bursa and removing (aspirating) some of the synovial fluid for examination can confirm the diagnosis. In most cases, the fluid will not be clear. It can be tested for the presence of microorganisms, which would indicate an infection, and crystals, which could indicate gout. In instances where the diagnosis is difficult, a local anesthetic (a drug that numbs the area) is injected into the painful spot. If the discomfort stops temporarily, then bursitis is probably the correct diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment of bursitis is usually effective. The application of heat, rest, and immobilization of the affected joint area is the first step. A sling can be used for a shoulder injury, a cane is helpful for hip problems. The patient can take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofin, and naproxen. They can be obtained without a prescription and relieve the pain and inflammation. Once the pain decreases, exercises of the affected area can begin. If the nearby muscles have become weak because of the disease or prolonged immobility, then exercises to build strength and improve movement are best. A doctor or physical therapist can prescribe an effective regimen. If the bursitis is related to an inflammatory condition like arthritis or gout, then management of that disease is needed to control the bursitis. When bursitis does not respond to conservative treatment, an injection into the joint of a long-acting corticosteroid preparation, like prednisone, can bring immediate and lasting relief. A corticosteroid is a hormonal substance that is the most effective drug for reducing inflammation. The drug is mixed with a local anesthetic and works on the joint within five minutes. Usually one injection is all that is needed.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely done strictly for treatment of a bursitis. If any underlying cause is the reason, this may be addressed surgically. During surgery for other conditions, a bursa may be seen and removed surgically.
Prevention
Continue to wear your orthotics for work and exercise to provide stability and restore foot function. Select suitable shoes for work and physical activity that provide stability for the heel. Regular stretching of the calf muscle can prevent heel bursitis. Do not suddenly increase activity amount without appropriate conditioning.
Hammer Toe Joint Fusion
 Overview
Overview
Hammer, claw, and mallet toes are toes that do not have the right shape. They may look odd or may hurt, or both. Tight shoes are the most common cause of these toe problems. A hammertoes is a toe that bends down toward the floor at the middle toe joint. It usually happens in the second toe. This causes the middle toe joint to rise up. Hammer toes often occur with bunions. Claw toe often happens in the four smaller toes at the same time. The toes bend up at the joints where the toes and the foot meet. They bend down at both the middle joints and at the joints nearest the tip of the toes. This causes the toes to curl down toward the floor. A mallet toe often happens to the second toe, but it may happen in the other toes as well. The toe bends down at the joint closest to the tip of the toe.
Causes
Most hammertoes are caused by wearing ill-fitting, tight or high-heeled shoes over a long period of time. Shoes that don?t fit well can crowd the toes, putting pressure on the middle toes and causing them to curl downward. Other causes include genes. Some people are born with hammertoe, bunions. These knobby bumps sometimes develop at the side of the big toe. This can make the big toe bend toward the other toes. The big toe can then overlap and crowd the smaller toes. Arthritis in a toe joint can lead to hammertoe.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Hammer toes can cause problems with walking and lead to other foot problems, such as blisters, calluses, and sores. Pain is caused by constant friction over the top of the toe?s main joint. It may be difficult to fit into some shoe gear due to the extra space required for the deformed toe. In many cases there will be pain on the ball of the foot over the metatarsals along with callus formation. This is due to the toes not functioning properly, failing to properly hammertoe touch the ground during the gait cycle. The ball of the foot then takes the brunt of the ground forces, which causes chronic pain.
Diagnosis
The earlier a hammertoe is diagnosed, the better the prognosis and treatment options. Your doctor will be able to diagnose your hammertoe with a simple examination of the foot and your footwear. He or she may take an x-ray to check the severity of the condition. You may also be asked about your symptoms, your normal daily activities, and your medical and family history.
Non Surgical Treatment
Your podiatrist may recommend one or more of these treatments to manage your hammer toes. Wear shoes with roomy toe boxes which don?t force your toes together. Exercises to stretch and strengthen muscles in the toes. Over the counter toe straps, cushions, and corn pads. Custom orthotic inserts. Toe caps or toe slings. In severe cases, surgery to release the muscles in the affected toes.
Surgical Treatment
Treatment of a severe hammertoe that has become rigid includes surgery. What is done during the surgery depends on how misshapen and inflexible the toe is. The surgeon may make a cut over your toe and release the tendon by cutting the tendon away from the bone. The surgeon may remove a small piece of bone from the toe. The surgeon may realign the tendons to reposition your toe or fasten the bones with pins. Sometimes the surgeon may have to join the bones in the toe. In this case, you will no longer be able to bend the toe, but the toe will be flat.
What Are The Most Obvious Key Causes Of Overpronation
Overview
Feet are supposed to roll inward as a part of every step you take. This helps them to mold to the various terrain that they step on (sand, rocks, various obstacles) without injury. This is called pronation. But, when your feet roll inward excessively, problems often arise. Excessive inward rolling of the feet and ankles is called over-pronation. Sometimes, people who over-pronate are told they have ?flat feet?. The term ?flat feet? can be misleading. When standing, body weight causes the arch of most feet to flatten out somewhat. This does not mean they become flat like pancakes (though some feet do). Instead, the arch shape gets longer and flatter and the arch height gets lower.

Causes
Acquired "Flat Feet" this develops over a period of time rather than at birth (unlike Congenital "Flat Feet"). In children, many different factors may contribute to the development of this condition such as the type of shoes that a child wears, a child's sitting or sleeping positions or it may occur as some type of compensation for other abnormalities located further up the leg. Compensation may occur due to the rupture (tearing) of ligaments or tendons in the foot. One common reason for this condition is that the foot is compensating for a tight Achilles Tendon. If this tendon is tight it may cause the foot to point downward away from the body. This gives the body the perception that the affected leg is longer in length and the body attempts to compensate for the perceived additional length by flattening out the foot arch in an attempt to provide balance and stability.
Symptoms
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. Here is a list of some of the common conditions associated with over-pronation in children. Achilles Pain. Ankle pain. Arch Pain. Low back pain. Heel Pain. Knee Pain (Runner's knee and Chondromalecia of the patella) Osgood Schlatter Disease (pain below the knee) Shin Splints (pain in the front of the lower leg) Over-pronation does not necessarily mean your child has "flat feet." Even though children's arches may be relatively high when they lie down or sit, over-pronation may not be seen until your child is standing. A certain amount of pronation is normal. During normal walking or running ("gait cycle"), the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward to absorb shock and adapt to the surface. This gait cycle is even more important if the running surface is uneven.
Diagnosis
Bunions, calluses and crooked toes may indicate alignment problems. So, it is important to ascertain the condition of a client's toes. Check the big toe to determine if the first joint of the toe is swollen, has a callus or bunion, and/or looks as though it abducts (i.e., hallux valgus) rather than pointing straight ahead. Also, look to see if the lesser toes seem to "curl up" (i.e., the person has hammer or claw toes). This may be indicative of damage to, or inflexibility of the plantar fascia caused by excessive flattening of the foot.

Non Surgical Treatment
When you see the doctor, he or she will likely perform a complete examination of your feet and watch you walk. The doctor will need to take x-rays to determine the cause of your flat feet. In some cases, further imaging may be needed, especially if your symptoms are severe and sudden in nature. Once you are properly diagnosed, your doctor will create an appropriate treatment plan. There are several options to correct overpronation, such as orthotics. In many cases, overpronation can be treated with non-surgical methods and over-the-counter orthotics. In severe cases, however, custom-made orthotics may work better. Orthotics provide arch support and therefore prevent collapse of the arch with weight bearing. They are made of materials such as spongy rubber or hard plastic. Your doctor will also want to examine your footwear to ensure they fit properly and offer enough medial support. Extra support and stability can be achieved with footwear that has a firm heel counter. If you are experiencing pain, you should be able to use over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen to relieve symptoms.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation-orthotics, for example-can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Severs Disease Physical Rehabilitation
Overview
Sever?s disease is also known as calcaneal apophysitis, which is a medical condition that causes heel pain In one or both feet. The disease is known to affect children between the ages of 8 and 14. Sever?s disease occurs when part of the child?s heel known as the growth plate (calcaneal epiphysis) is attached to the Achilles tendon. This area can suffer injury when the muscles and tendons of the growing foot do not keep pace with bone growth. Therefore, the constant pain which one experiences at the back of the heel will make the child unable to put any weight on the heel. The child is then forced to walk on their toes. Toe gait- develops in which the child must change the way they walk to avoid placing weight on the heel. This can lead to other problems as well in the future.
Causes
Sever?s disease is often an overuse injury. It can be caused by playing sports, especially those involving high impact. Sever?s disease can also be linked to growth which can place a stress on the attachment of the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
As a parent, you may notice your child limping while walking or running awkwardly. If you ask them to rise onto their tip toes, their heel pain usually increases. Heel pain can be felt in one or both heels in Sever's disease.
Diagnosis
This condition is self limiting, it will go away when the two parts of bony growth join together, this is natural. Unfortunately, Sever's disease can be very painful and limit sport activity of the child while waiting for it to go away, so treatment is often advised to help relieve it. In a few cases of Sever's disease, the treatment is not successful and these children will be restricted in their activity levels until the two growth areas join, usually around the age of 16 years. There are no known long term complications associated with Sever's disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
It is important that those with Sever?s Disease are treated by a medical professional to reduce pain and allow children to continue to participate in sporting activities. The Athlete?s Foot recommends a visit to your local medical professional to be diagnosed correctly and receive specialised care. Symptoms include pain through the back of the heel where the Achilles tendon inserts into the heel bone, pain during activity especially running and jumping and the back of the heel may be tender to touch.
What Causes Achilles Tendonitis Discomfort ?
Overview
 Inflammation of the Achilles tendon.The Achilles is the large tendon connecting the two major calf muscles, gastrocnemius and soleus, to the back of the heel bone. Under too much stress, the tendon tightens and is forced to work too hard. This causes it to become inflamed (that is tendinitis), and, over time, can produce a covering of scar tissue, which is less flexible than the tendon. If the inflamed Achilles continues to be stressed, it can tear or rupture.
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon.The Achilles is the large tendon connecting the two major calf muscles, gastrocnemius and soleus, to the back of the heel bone. Under too much stress, the tendon tightens and is forced to work too hard. This causes it to become inflamed (that is tendinitis), and, over time, can produce a covering of scar tissue, which is less flexible than the tendon. If the inflamed Achilles continues to be stressed, it can tear or rupture.
Causes
Hill running or stair climbing. Overuse resulting from the natural lack of flexibility in the calf muscles. Rapidly increasing mileage or speed. Starting up too quickly after a layoff. Trauma caused by sudden and hard contraction of the calf muscles when putting out extra effort such as in a final sprint. Achilles tendinitis often begins with mild pain after exercise or running that gradually worsens.
Symptoms
Mild ache in the back of the lower leg, especially after running. More acute pain may occur after prolonged activity, Tenderness or stiffness in the morning. In most cases the pain associated with Achilles tendinitis is more annoying than debilitating, making sufferers regret activity after the fact, but not keeping them from doing it. More severe pain around the Achilles tendon may be a symptom of a much more serious ruptured tendon.
Diagnosis
In diagnosing Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis, the surgeon will examine the patient?s foot and ankle and evaluate the range of motion and condition of the tendon. The extent of the condition can be further assessed with x-rays or other imaging modalities.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment depends on severity of pain. The most effective long-term treatment for Achilles tendinitis/tendinopathy is physical therapy, particularly therapy that focuses on eccentric muscle/tendon strengthening. Calf and Achilles stretching are also an important part of the treatment. In severe cases, treatment may begin with a period of rest and immobilization in order to calm down the tendon before physical therapy is initiated. Anti-inflammatories may be prescribed. Avoiding activities that aggravate the Achilles tendon will help the healing process. Improvement and resolution of symptoms can take months. Exercise might be the cause of Achilles tendonitis, but it can also help prevent it and aid in recovery. Healing will occur more quickly if there is no pressure on the injured tendon, and if the foot is at least partially immobilized.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery usually isn't needed to treat Achilles tendinopathy. But in rare cases, someone might consider surgery when rubbing between the tendon and the tissue covering the tendon (tendon sheath) causes the sheath to become thick and fibrous. Surgery can be done to remove the fibrous tissue and repair any small tendon tears. This may also help prevent an Achilles tendon rupture.
Prevention
There are several things you can do to reduce the risk of Achilles tendinitis, warm up every time before you exercise or play a sport. Switch up your exercises. Slowly increase the length and intensity of your workouts. Keep your muscles active and stay in shape all year-round. When you see symptoms of Achilles tendinitis, stop whatever activity you are doing and rest.
What Will Cause Painful Heel And Approaches To Successfully Treat It

Overview
If you experience sharp, throbbing or aching heel pain with your first steps out of bed each morning, or when walking throughout the day, you may be suffering from Plantar Fasciitis. This guide will help you to understand the definition, symptoms and causes of this condition and will explore your treatment options for rapid relief from your pain.
Causes
It usually starts following an increase in activity levels. Increase in weight. Standing for long periods. Poor footwear. Tight muscle groups. Abnormal pressure on the plantar Fascia can be caused by any of the above. The plantar fascia becomes inflamed and tiny rips can occur where it attaches into the inside of the heel bone. The area becomes inflamed and swollen, and it is the increase in fluid to the area that accumulates when weight is taken off the area that then causes the pain on standing.
Symptoms
Plantar fascia usually causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel although some people have heel spurs and suffer no symptoms at all. Occasionally, heel pain is also associated with other medical disorders such as arthritis (inflammation of the joint), bursitis (inflammation of the tissues around the joint). Those who have symptoms may experience ‘First step’ pain (stone bruise sensation) after getting out of bed or sitting for a period of time. Pain after driving. Pain on the bottom of your heel. Deep aching pain. Pain can be worse when barefoot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is based on a medical history, the nature of symptoms, and the presence of localised tenderness in the heel. X-rays may be recommended to rule out other causes for the symptoms, such as bone fracture and to check for evidence of heel spurs. Blood tests may also be recommended.
Non Surgical Treatment
Talk to your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Options include. Apply ice or a cold pack to the heel and arch for 15 to 20 minutes several times a day. Wrap the ice or cold pack in a towel. Do not apply the ice directly to your skin. A special splint that will hold your foot in a neutral position while sleeping. Special shoe inserts that support the mid-arch region of your foot. Inserts that are not customized may work just as well as those that are customized. Activity. Avoid running and other activities that may worsen pain. Begin stretching exercises to lengthen the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia as recommended by your doctor. This is usually done when pain has lessened or improved. To help manage pain, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Prescription pain relievers may also be required. Steroid injections may be used in some cases or if other treatment is not working. A special type of sound wave called extracorporeal shock wave may also be considered in certain cases. This treatment happens under the care of your doctor. At this time, this is generally a treatment for long-term cases that do not respond to other treatments. Massage therapy or accupuncture may also be effective for long-term cases. In a few cases, basic treatments don't help. Surgery may be performed to cut the tight, swollen fascia.

Surgical Treatment
When more conservative methods have failed to reduce plantar fasciitis pain, your doctor may suggest extracorporeal shock wave therapy, which is used to treat chronic plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy uses sound waves to stimulate healing, but may cause bruises, numbness, tingling, swelling, and pain. When all else fails, surgery may be recommended to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone. Few people need surgery to treat the condition.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises for your foot are important. Do the stretches shown here at least twice a day. Don't bounce when you stretch. Plantar fascia stretch. To do the plantar fascia stretch, stand straight with your hands against a wall and your injured leg slightly behind your other leg. Keeping your heels flat on the floor, slowly bend both knees. You should feel the stretch in the lower part of your leg. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Calf stretch. Stand with your hands against a wall and your injured leg behind your other leg. With your injured leg straight, your heel flat on the floor and your foot pointed straight ahead, lean slowly forward, bending the other leg. You should feel the stretch in the middle of your calf. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Other exercises. You can also strengthen your leg muscles by standing on the ball of your foot at the edge of a step and raising up as high as possible on your toes. Relax between toe raises and let your heel fall a little lower than the edge of the step. It's also helpful to strengthen the foot by grabbing a towel with your toes as if you are going to pick up the towel with your foot. Repeat this exercise several times a day.
What Is Pain Under The Heel And The Right Way To Overcome It

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It involves pain and inflammation of a thick band of tissue, called the plantar fascia, that runs across the bottom of your foot and connects your heel bone to your toes. Plantar fasciitis commonly causes stabbing pain that usually occurs with your very first steps in the morning. Once your foot limbers up, the pain of plantar fasciitis normally decreases, but it may return after long periods of standing or after getting up from a seated position. Plantar fasciitis is particularly common in runners. In addition, people who are overweight and those who wear shoes with inadequate support are at risk of plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Because the plantar fascia supports your foot and gets used every time you take a step, it has to absorb a large amount of stress and weight. If too much pressure is put on the plantar fascia, the fibers can become damaged or start to tear. The body responds by causing inflammation in the affected area. This is what causes the pain and stiffness of plantar fasciitis. Things that can increase the risk of plantar fasciitis include tight calf muscles. Tight calves make it harder to flex your foot, and this puts more stress on the plantar fascia. Weight. Carrying a few extra pounds puts added pressure on your feet every time you take a step. Activities that put a lot of stress on the feet. This includes things like running, hiking, dancing, and aerobics. Bad shoes. Footwear that doesn't give your foot the support it needs increases your risk of plantar fasciitis. You'll want to ditch any shoes that have thin soles or inadequate arch support, or ones that don't fit your feet properly. Routinely wearing high heels can also cause your Achilles tendon to contract over time, making it harder to flex your foot. Jobs that involve a lot of standing or walking on hard surfaces. Jobs that keep you on your feet all day, like waiting tables or working in a store, can cause damage to your plantar fascia. High arches, flat feet, or other foot problems. The shape of your foot can affect the way your weight is distributed on your feet when you stand. If weight distribution is a bit off, it can add to a person's risk of plantar fasciitis. How someone walks can increase the stress on certain parts of the foot too.
Symptoms
The classic sign of plantar fasciitis is that the worst pain occurs with the first few steps in the morning, but not every patient will have this symptom. Patients often notice pain at the beginning of activity that lessens or resolves as they warm up. The pain may also occur with prolonged standing and is sometimes accompanied by stiffness. In more severe cases, the pain will also worsen toward the end of the day.
Diagnosis
A physical exam performed in the office along with the diagnostic studies as an x-ray. An MRI may also be required to rule out a stress fracture, or a tear of the plantar fascia. These are conditions that do not normally respond to common plantar fasciitis treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
In the early stages of plantar fasciitis resting the foot may ease the pain. Medication to reduce inflammation should help but should only be used short term. Strapping may temporarily reduce the pain. All of the above therapies are only temporary measures and the pain is likely to reoccur if the cause of the abnormal pressure which has triggered the plantar fasciitis has not been identified. In order to establish the cause of the plantar fasciitis a biomechanical assessment may be required.
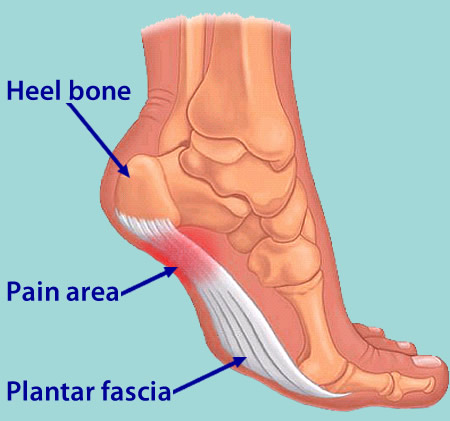
Surgical Treatment
Like every surgical procedure, plantar fasciitis surgery carries some risks. Because of these risks your doctor will probably advise you to continue with the conventional treatments at least 6 months before giving you approval for surgery. Some health experts recommend home treatment as long as 12 months. If you can’t work because of your heel pain, can’t perform your everyday activities or your athletic career is in danger, you may consider a plantar fasciitis surgery earlier. But keep in mind that there is no guarantee that the pain will go away completely after surgery. Surgery is effective in many cases, however, 20 to 25 percent of patients continue to experience heel pain after having a plantar fasciitis surgery.
What Exactly Causes Pain At The Heel
Overview
If your first step in the morning often feels like it involves a rusty nail being inserted into your heel, you’re not alone. Heel pain resulting from plantar fasciitis is the most prevalent condition treated in podiatric clinics, and an additional 1 million Americans annually are seen by medical doctors for the condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The plantar fascia is the ligament that runs from the heel bone across the entire bottom of the foot and connects at the base of the toes. Ligaments connect bone to bone, and don’t really constrict or contract, but can become thickened because of inflammation. Inflammation of the plantar fascia can cause strain when you walk, specifically heel pain that is especially bad for the first few steps after prolonged inactivity. It then typically loosens up once you’re up and about.
Causes
It is common to see patients with Plantar Fasciitis who have been wearing shoes that are too soft and flexible. The lack of support can be stressful on the heel for those patients who’s feet aren’t particularly stable. If these ill fitting shoes are worn for long enough, the stress will lead to Heel Pain as the inflammation of the fascia persists. Footwear assessment and advice will be essential in order to get on top of the Plantar Fasciitis. It may surprise some people to learn that high heeled shoes are not the cause of Plantar Fasciitis, although they can cause tight calf muscles. High arches can lead to Plantar Fasciitis. This is due to the lack of contact under the sole of the foot. Even sports shoes which appear to have good arch support inside are often too soft and not high enough to make contact with the arch of the foot. Hence, the plantar fascia is unsupported. This can lead to Heel pain and Plantar Fasciitis. Flat feet can lead to Plantar Fasciitis. Flat feet is caused by ligament laxity and leads to foot instability. Other structures such as muscles, tendons and fascia work harder to compensate for this instability. Heel pain or Plantar Fasciitis arises when the instability is too great for these other structures to cope with. The strain on the fascia is too severe and the inflammation sets in. Over stretching can lead to Plantar Fasciitis. Certain calf stretches put the foot into a position that creates a pulling sensation through the sole of the foot. This can cause Plantar Fasciitis which can cause pain in the arch of the foot as well as Heel Pain.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis has a few possible symptoms. The symptoms can occur suddenly or gradually. Not all of the symptoms must be present at once. The classic symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain around the heel with the first few steps out of bed or after resting for a considerable period of time. This pain fades away a few minutes after the feet warm up. This symptom is so common that it symbols the plantar fasciitis disorder. If you have it then probably you have plantar fasciitis. If you don’t suffer from morning pain then you might want to reconsider your diagnosis. Pain below the heel bone at the connection of the bone to the fascia. As the condition becomes more severe the pain can get more intense during the day without rest. Plantar fasciitis symptoms include pain while touching the inside of the heel or along the arch. Foot pain after you spend long periods of time standing on your feet. Pain when stretching the plantar fascia. Foot pain that worsens when climbing stairs or standing on the toes. Pain that feels as though you are walking on glass. Pain when you start to exercise that gets better as you warm up but returns after you stop.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications can help decrease the inflammation in the arch and heel of your foot. These medications include Advil, Mtrin, Ibuprofen, and Aleve. Use the medication as directed on the package. If you tolerate it well, take it daily for two weeks then discontinue for one week. If symptoms worsen or return, resume for two weeks, then stop. You should eat when taking these medications, as they can be hard on your stomach. Ach Support. Over the counter inserts provide added arch support and soft cushion. Based on the individual needs of your foot, you may require custom inserts. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Pace a shoe insert under your affected foot. Place your affected leg behind your unaffected leg with the toes of your back foot pointed towards the heel of your other foot. Lean into the wall. Bend your front knee while keeping your back leg straight with your heel firmly on the ground. Hold the stretch for a count of 10. A set is 10 repetitions. Perform the stretch at least three times a day.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered only after 12 months of aggressive nonsurgical treatment. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the plantar fascia, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite a year of calf stretches. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope, an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Plantar fascia release. If you have a normal range of ankle motion and continued heel pain, your doctor may recommend a partial release procedure. During surgery, the plantar fascia ligament is partially cut to relieve tension in the tissue. If you have a large bone spur, it will be removed, as well. Although the surgery can be performed endoscopically, it is more difficult than with an open incision. In addition, endoscopy has a higher risk of nerve damage.
Stretching Exercises
In one exercise, you lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and heel on the ground. Your other knee is bent. Your heel cord and foot arch stretch as you lean. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times for each sore heel. It is important to keep the knee fully extended on the side being stretched. In another exercise, you lean forward onto a countertop, spreading your feet apart with one foot in front of the other. Flex your knees and squat down, keeping your heels on the ground as long as possible. Your heel cords and foot arches will stretch as the heels come up in the stretch. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times. About 90 percent of people with plantar fasciitis improve significantly after two months of initial treatment. You may be advised to use shoes with shock-absorbing soles or fitted with an off-the-shelf shoe insert device like a rubber heel pad. Your foot may be taped into a specific position. If your plantar fasciitis continues after a few months of conservative treatment, your doctor may inject your heel with steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. If you still have symptoms, you may need to wear a walking cast for two to three weeks or a positional splint when you sleep. In a few cases, surgery is needed for chronically contracted tissue.
What Exactly Triggers Plantar Fasciitis

Overview
The plantar fascia is a thickened fibrous aponeurosis that originates from the medial tubercle of the calcaneus, runs forward to insert into the deep, short transverse ligaments of the metatarsal heads, dividing into 5 digital bands at the metatarsophalangeal joints and continuing forward to form the fibrous flexor sheathes on the plantar aspect of the toes. Small plantar nerves are invested in and around the plantar fascia, acting to register and mediate pain.
Causes
This is a problem of either extreme, so people with high arches or those that have very flat feet are at risk of developing pain in this region. This is because of the relative stress the plantar fascia is put under. In people with excessive pronation, the plantar fascia is put under too much stretch, as their range flattens and strains it. People with a stiff, supinated (high-arched) foot lack the flexibility to appropriately shock absorb, so this too puts extra strain on the plantar fascia. Clinically, we see more people presenting with plantar fascia pain who have excessive pronation than those with stiff, supinated feet. But while the foot type is the biggest risk factor for plantar fasciitis, the whole leg from the pelvis down can affect how the foot hits the ground. A thorough biomechanical assessment will determine where in the kinetic chain things have gone wrong to cause the overload.
Symptoms
The pain is more intense with your first steps out of bed in the morning or after sitting for a while. The reason for this is that during rest our muscles and ligaments tend to shorten and tighten up. The tightening of the plantar fascia means more traction on the ligament making the tissue even more sensitive. With sudden weight-bearing the tissue is being traumatised, resulting in a stabbing pain. After walking around for a while the ligament warms up, becomes a little bit more flexible and adapts itself, making the pain go way entirely or becoming more of a dull ache. However, after walking a long distance or standing for hours the pain will come back again. To prevent the sudden sharp pain in the morning or after sitting, it is important to give the feet a little warm-up first with some simple exercises. Also, any barefoot walking should be avoided, especially first thing in the morning, as this will damage to the plantar fascia tissue. Aparty from pain in the heel or symptoms may include a mild swelling under the heel. In addition, heel pain is often associated with tightness in the calf muscles. Tight calf muscles are a major contributing factor to Plantar Fasciitis.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check your feet and watch you stand and walk. He or she will also ask questions about your past health, including what illnesses or injuries you have had. Your symptoms, such as where the pain is and what time of day your foot hurts most. How active you are and what types of physical activity you do. Your doctor may take an X-ray of your foot if he or she suspects a problem with the bones of your foot, such as a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter arch supports may be useful in patients with acute plantar fasciitis and mild pes planus. The support provided by over-the-counter arch supports is highly variable and depends on the material used to make the support. In general, patients should try to find the most dense material that is soft enough to be comfortable to walk on. Over-the-counter arch supports are especially useful in the treatment of adolescents whose rapid foot growth may require a new pair of arch supports once or more per season. Custom orthotics are usually made by taking a plaster cast or an impression of the individual's foot and then constructing an insert specifically designed to control biomechanical risk factors such as pes planus, valgus heel alignment and discrepancies in leg length. For patients with plantar fasciitis, the most common prescription is for semi-rigid, three-quarters to full-length orthotics with longitudinal arch support. Two important characteristics for successful treatment of plantar fasciitis with orthotics are the need to control over-pronation and metatarsal head motion, especially of the first metatarsal head. In one study, orthotics were cited by 27 percent of patients as the best treatment. The main disadvantage of orthotics is the cost, which may range from $75 to $300 or more and which is frequently not covered by health insurance.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not needed for plantar fasciitis. About 95 out of 100 people who have plantar fasciitis are able to relieve heel pain without surgery. Your doctor may consider surgery if non-surgical treatment has not helped and heel pain is restricting your daily activities. Some doctors feel that you should try non-surgical treatment for at least 6 months before you consider surgery. The main types of surgery for plantar fasciitis are Plantar fascia release. This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament . This releases the tension on the ligament and relieves inflammation . Other procedures, such as removing a heel spur or stretching or loosening specific foot nerves. These surgeries are usually done in combination with plantar fascia release when there is lasting heel pain and another heel problem. Experts in the past thought that heel spurs caused plantar fasciitis. Now experts generally believe that heel spurs are the result, not the cause, of plantar fasciitis. Many people with large heel spurs never have heel pain or plantar fasciitis. So surgery to remove heel spurs is rarely done.
Workout Routines For Football Inuries to the Foot and Ankle
Did you know that redheads require 20% more general anesthesia than non-gingers before going under the knife? Often taken for granted, our feet and ankles are subjected to a rigorous workout everyday. Pain, such as may occur in our heels, alerts Bunion Pain us to seek medical attention. The fungal problems seen most often are athlete's foot and fungus nails. Big toe joint pain can be a warning sign of arthritis. Enter the shape, color, or imprint of your prescription or OTC drug. Help!!!!!
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
Those affected by inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Achilles tendonitis are also likely to experience pain and swelling in the ankles. If the joints in the feet get affected by osteoarthritis, it gives rise to pain, stiffness, swelling in or around the joint, and restricted range of motion. Since pain in the feet could be caused due to a variety of reasons, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Many a time, pain could be experienced by people who perform high-impact exercises such as running, jogging and other sports. Those who have been experiencing pain while running must make sure that they wear a good quality footwear. Painkillers or steroids might be prescribed for the treatment of a sprained ankle.

The spur occurs where the plantar fascia attaches, and the pain in that area is really due to the plantar fascia attachment being irritated. However, there are many people with heel spurs who have no symptoms at all. Haglund's deformity is a bony growth on the back of the heel bone, which then irritates the bursa and the skin lying behind the heel bone. Achilles tendinopathy is degeneration of the tendon that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. Stress fractures are common in military training.

Bunions are bony lumps that develop on the side of your foot and at the base of your big toe. They're the result of a condition called hallux valgus, which causes your big toe joint to bend towards your other toes and become may also develop a bursa here too, especially if your shoes press against the bunion. Sometimes swellings or bursae on the joints in your feet are also called bunions, but these aren't the same as bunions caused by hallux valgus. Hallux valgus is different to hallux rigidus, which is osteoarthritis of the big toe joint. Hallux rigidus causes your big toe to become stiff and its range of movement is reduced. Symptoms of a bunion can be controlled by choosing shoes with a soft, wide upper to reduce pressure and rubbing on your joint. Toes form hammer or claw shape.
Achilles Tendonitis Facts
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles (uh-KIL-eez) tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Under too much stress, the tendon tightens and is forced to work too hard. This causes it to become inflamed (that?s Achilles tendinitis), and, over time, can produce a covering of scar tissue, which is less flexible than the tendon. If the inflamed Achilles continues to be stressed, it can tear or rupture. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It?s also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor?s supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles (uh-KIL-eez) tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Under too much stress, the tendon tightens and is forced to work too hard. This causes it to become inflamed (that?s Achilles tendinitis), and, over time, can produce a covering of scar tissue, which is less flexible than the tendon. If the inflamed Achilles continues to be stressed, it can tear or rupture. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It?s also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor?s supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Causes
Like any muscle or tendon in the body, the older we get, the more likely we are to sustain an injury. So middle-aged men and women are most at risk, with a slightly higher risk factor attributed to males. Those who participate in more intense athletic activities like high impact sports (tennis, running, basketball) are most susceptible to the injury. Certain underlying medical conditions can also be a contributing factor. Diabetics are more at risk of suffering from Achilles Tendinitis, as are those who are not in great physical shape. Some antibiotics, particularly fluoroquinolones can make one more likely to suffer a strained Achilles Tendon.
Symptoms
The main symptom of Achilles tendonitis is a feeling of pain and swelling in your heel as you walk or run. Other symptoms include tight calf muscles and limited range of motion when flexing the foot. This condition can also make the skin in your heel feel overly warm to the touch.
Diagnosis
If Achilles tendonitis is suspected, avoid any exercise or activity that causes the pain. It is advisable to see a doctor promptly so that an accurate diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment recommended. The doctor will take a full medical history and will ask about the nature and duration of the symptoms. They will perform a physical examination of the affected area. Ultrasound scanning may be used to assess damage to the tendon or surrounding structures. Occasionally MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be recommended. The symptoms of Achilles tendonitis are often similar to symptoms of other conditions such as partial Achilles tendon rupture and heel bursitis. This can make diagnosis difficult and a referral to an orthopaedic specialist may be required in order for an accurate diagnosis to be made.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Nonsurgical methods include rest and stop doing activities that cause stress to the tendon. Ice the area by applying ice to the tendon for 15 minutes after exercising. Compress the tendon by using an athletic wrap or surgical tape. Elevate your injury. You can reduce swelling by lying down and raising your foot at a level that is above your heart. Stretch your ankles and calf muscles. Take anti-inflammatory medication (e.g.: ibuprofen to reduce swelling). Wear orthotics and running shoes. Take part in physical therapy.

Surgical Treatment
Occasionally, conservative management of Achilles tendon conditions fails. This failure is more common in older male patients and those with longstanding symptoms, those who persist in full training despite symptoms or those who have uncorrected predisposing factors. In these cases, surgery may be indicated. It should be remembered, however, that the rehabilitation program, particularly for severe Achilles tendon injuries, is a slow, lengthy program. Surgery is only indicated when there is failure to progress in the rehabilitation program. Surgery should not be considered unless at least six months of appropriate conservative management has failed to lead to improvement.
Prevention
Wear shoes that fit correctly and support your feet: Replace your running or exercise shoes before the padding or shock absorption wears out. Shock absorption greatly decreases as the treads on the bottoms or sides of your shoes begin to wear down. You may need running shoes that give your foot more heel or arch support. You may need shoe inserts to keep your foot from rolling inward. Stretch before you exercise: Always warm up your muscles and stretch gently before you exercise. Do cool down exercises when you are finished. This will loosen your muscles and decrease stress on your Achilles tendon. Exercise the right way: If your tendinitis is caused by the way that you exercise, ask a trainer, coach, or your caregiver for help. They can teach you ways to train or exercise to help prevent Achilles tendinitis. Do not run or exercise on uneven or hard surfaces. Instead, run on softer surfaces such as treadmills, rubber tracks, grass, or evenly packed dirt tracks.